| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- MVVM
- 리엑트
- HTML
- 오류
- Animation
- 자바스크립트
- page
- AnimationController
- 함수
- Binding
- MSSQL
- 깃허브
- 닷넷
- Maui
- Firebase
- 파이어베이스
- 플러터
- spring boot
- db
- React JS
- JavaScript
- MS-SQL
- .NET
- GitHub
- 바인딩
- Flutter
- 마우이
- 애니메이션
- typescript
- listview
- Today
- Total
개발노트
5. [Spring Boot] JPA 로 삽입, 조회, 수정, 삭제 기능 만들기(with ResponsEntity) 본문
5. [Spring Boot] JPA 로 삽입, 조회, 수정, 삭제 기능 만들기(with ResponsEntity)
mroh1226 2024. 4. 16. 16:42JPA를 이용하여 삽입, 조회, 수정, 삭제 등 API 호출 기능을 만들어 보겠습니다.
여기에 ResponsEntity를 이용하여 http 상태코드에 따른 응답도 만들어봅니다.
만들어볼 기능들
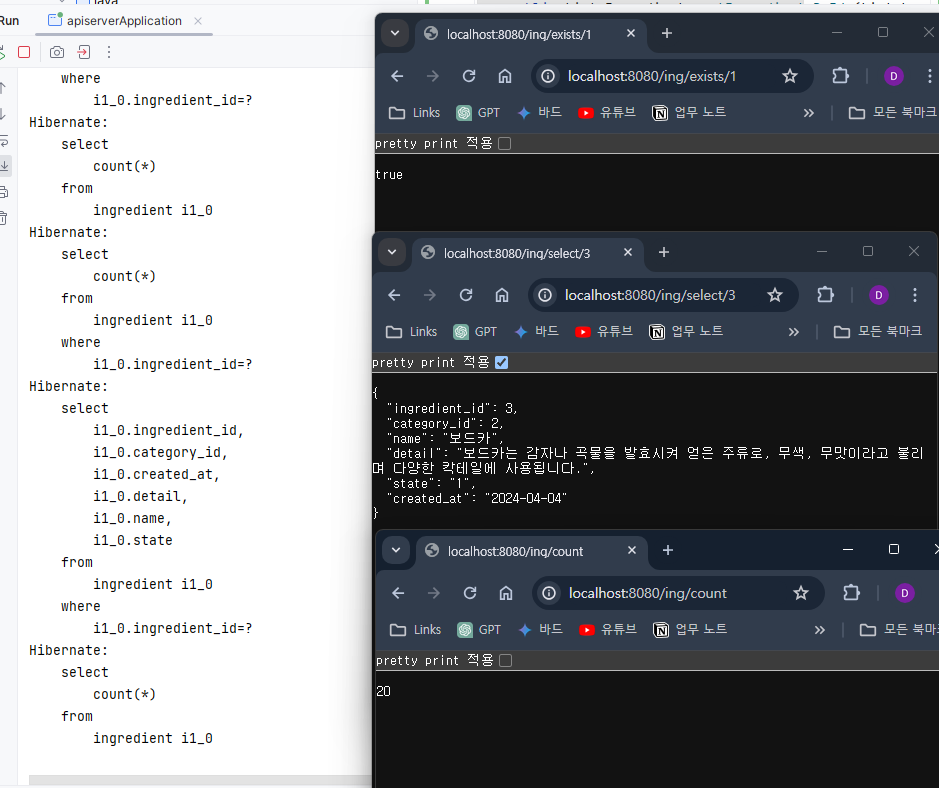
예시로 사용될 Ingredient 모델과 리포지토리
Ingredient.java (Model)
package com.homebar.apiserver.model;
import jakarta.persistence.*;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
import org.springframework.format.annotation.DateTimeFormat;
import java.util.Date;
@Entity
//어노테이션이 있으면 Getter,Setter 자동 생성
@Getter
@Setter
@Table(name = "Ingredient")
public class Ingredient {
//@Id:Primary Key 설정
@Id
//@GeneratedValue: 자동으로 생성되는 것을 나타냄,IDENTITY는 자동 증가를 나타냄
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long ingredient_id;
//@Column: 엔티티의 필드명과 데이터베이스 테이블의 컬럼명이 다를 때 또는 컬럼의 길이,
// NULL 허용 여부 등과 같은 속성을 지정해야 할 때 @Column 어노테이션을 사용
@Column(name = "category_id",nullable = false)
private Long category_id;
@Column(name = "name",length = 255)
private String name;
@Column(name = "detail",length = 255)
private String detail;
//precision: 정수의 전체 자릿수, scale: 소수점 이하의 자릿수
@Column(name = "state",precision = 1)
private String state;
@Column(name = "created_at")
@Temporal(TemporalType.DATE)
@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd")
private Date created_at;
}IngredientRepository.java (Repository)
package com.homebar.apiserver.repository;
import com.homebar.apiserver.model.Ingredient;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public interface IngredientRepository extends JpaRepository<Ingredient,Long> {
}
위 Ingredient라는 Entity를 이용하여 JPA 메소드를 하나하나 만들어보겠습니다.
아래 설명될 예시들은 Service와 Controller에 작성될 예시들 입니다.
JPA 메소드 종류
- findAll(): 모든 데이터 조회
- 설명: 데이터베이스에서 모든 레코드를 검색하여 반환합니다.
- 사용 예시: 모든 사용자 정보를 검색하여 반환하거나, 모든 주문 목록을 검색하여 반환하는 등의 경우에 사용됩니다.
- 반환 값: 데이터베이스에서 검색된 모든 레코드가 컬렉션(List, 배열 등) 형태로 반환됩니다.
IngredientService.java 👉🏻 이하, Service
//조회(모든 데이터)
public List<Ingredient> getAllIngredients(){
//단일 객체가 아닌 List는 Optional 안써도 됨,
List<Ingredient> ingredients = ingredientRepository.findAll();
if(ingredients == null){
throw new RuntimeException("Ingredients is Empty");
}
return ingredients;
}IngredientController.java 👉🏻 이하, Controoler
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/ing")
public class IngredientController {
@Autowired
private IngredientService ingredientService;
@GetMapping("/all")
public ResponseEntity<List<Ingredient>> getAllIngredients(){
List<Ingredient> ingredients = ingredientService.getAllIngredients();
if(ingredients.isEmpty()){
return ResponseEntity.noContent().build();
}
else {
return ResponseEntity.ok(ingredients);
}
}
- findById(): Id로 데이터 조회
- 설명: 데이터베이스에서 주어진 ID에 해당하는 레코드를 검색하여 반환합니다.
- 사용 예시: 특정 사용자의 ID를 기반으로 해당 사용자의 정보를 검색하거나, 특정 제품의 ID를 기반으로 해당 제품의 정보를 검색하는 등의 경우에 사용됩니다.
- 반환 값: 주어진 ID에 해당하는 레코드가 단일 객체 형태로 반환됩니다.
Service
//조회(id로 단일 조회)
public Optional<Ingredient> getIngredientById(Long id){
//단일 객체에는 Optional을 사용해서 null 오류를 미리 방지함
if(id <= 0){
return Optional.empty();
}else{
return ingredientRepository.findById(id);
}
}Controller
@GetMapping("/select/{ingredient_id}")
public ResponseEntity<Ingredient> getIngredientById(@PathVariable("ingredient_id") Long ingredientId){
Optional<Ingredient> ingredient = ingredientService.getIngredientById(ingredientId);
return ingredient.map(ResponseEntity::ok)
.orElse(ResponseEntity.notFound().build());
}
- save(): 데이터 Upsert
- 설명: 새로운 레코드를 생성하거나 기존 레코드를 업데이트합니다.
- 사용 예시: 새로운 사용자를 데이터베이스에 추가하거나, 기존 사용자의 정보를 업데이트하는 등의 경우에 사용됩니다.
- 반환 값: 저장 또는 업데이트된 객체를 반환합니다.
Service
//삽입, 업데이트 (Upsert)
public Ingredient upsertIngredient(Ingredient ingredient){
return ingredientRepository.save(ingredient);
}Controller
@PostMapping("/upsert")
public ResponseEntity<Ingredient> upsertIngredient(@RequestBody Ingredient ingredient){
Ingredient result = ingredientService.upsertIngredient(ingredient);
return ResponseEntity.ok(result);
}
- delete(): 데이터 삭제
- 설명: 주어진 ID 또는 객체에 해당하는 레코드를 데이터베이스에서 삭제합니다.
- 사용 예시: 특정 사용자의 ID를 기반으로 해당 사용자를 삭제하거나, 특정 주문의 객체를 기반으로 해당 주문을 삭제하는 등의 경우에 사용됩니다.
- 반환 값: 삭제된 레코드의 수 또는 삭제 작업의 성공 여부를 반환할 수 있습니다.
Service
//삭제(id로 데이터 삭제)
public void deleteIngredient(Long id){
ingredientRepository.deleteById(id);
}Controller
@DeleteMapping("/delete/{ingredient_id}")
public ResponseEntity<Void> deleteIngredient(@PathVariable ("ingredient_id") Long ingredientId){
ingredientService.deleteIngredient(ingredientId);
return ResponseEntity.noContent().build();
}
- count(): 데이터 갯수 조회
- 설명: 데이터베이스에서 특정 조건을 만족하는 레코드의 개수를 반환합니다.
- 사용 예시: 특정 조건을 만족하는 사용자의 수를 세거나, 특정 기간 동안의 주문 수를 세는 등의 경우에 사용됩니다.
- 반환 값: 조건을 만족하는 레코드의 개수를 반환합니다.
Service
// 데이터 갯수 조회
public long countIngredients() {
return ingredientRepository.count();
}Controller
@GetMapping("/count")
public long countIngredients() {
return ingredientService.countIngredients();
}
- existsById(): 존재여부 조회
- 설명: 주어진 ID에 해당하는 레코드가 데이터베이스에 존재하는지 여부를 확인합니다.
- 사용 예시: 특정 ID를 가진 사용자가 데이터베이스에 존재하는지 여부를 확인하는 등의 경우에 사용됩니다.
- 반환 값: 주어진 ID에 해당하는 레코드가 존재하면 true를 반환하고, 그렇지 않으면 false를 반환합니다.
Service
// 존재 여부 조회
public boolean doesIngredientExist(Long id) {
return ingredientRepository.existsById(id);
}Controller
@GetMapping("/exists/{ingredient_id}")
public boolean doesIngredientExist(@PathVariable("ingredient_id") Long ingredientId) {
return ingredientService.doesIngredientExist(ingredientId);
}
- findAllById(): 여러개의 Id 로 데이터 조회
- 설명: 주어진 ID 목록에 해당하는 모든 레코드를 검색하여 반환합니다.
- 사용 예시: 여러 사용자의 ID 목록을 기반으로 해당 사용자들의 정보를 검색하거나, 여러 제품의 ID 목록을 기반으로 해당 제품들의 정보를 검색하는 등의 경우에 사용됩니다.
- 반환 값: 주어진 ID 목록에 해당하는 모든 레코드가 컬렉션 형태로 반환됩니다.
Service
// 여러개의 Id로 데이터 조회
public List<Ingredient> getIngredientsByIds(List<Long> ids) {
return ingredientRepository.findAllById(ids);
}Controller
@GetMapping("/find-by-ids")
public ResponseEntity<List<Ingredient>> getIngredientsByIds(@RequestParam List<Long> ids) {
List<Ingredient> ingredients = ingredientService.getIngredientsByIds(ids);
if (ingredients.isEmpty()) {
return ResponseEntity.noContent().build();
} else {
return ResponseEntity.ok(ingredients);
}
}
- deleteAll(): 모든 데이터 삭제
- 설명: 데이터베이스에서 모든 레코드를 삭제합니다.
- 사용 예시: 특정 테이블의 모든 데이터를 삭제하는 등의 경우에 사용됩니다.
- 반환 값: 삭제된 레코드의 수 또는 삭제 작업의 성공 여부를 반환할 수 있습니다.
Service
// 모든 데이터 삭제
public void deleteAllIngredients() {
ingredientRepository.deleteAll();
}Controller
@DeleteMapping("/delete/all")
public void deleteAllIngredients() {
ingredientService.deleteAllIngredients();
}
이러한 메서드는 대부분의 데이터베이스 액세스 라이브러리나 ORM(Object-Relational Mapping) 프레임워크에서 제공됩니다. 이를 사용하여 애플리케이션에서 데이터를 읽고 쓰고 삭제할 수 있습니다. 데이터베이스의 특정 테이블에 대한 CRUD(Create, Read, Update, Delete) 연산을 수행할 때 자주 사용됩니다.
Spring Boot로 API를 개발할 때 클라이언트에게 적절한 응답을 보내는 것은 매우 중요합니다. ResponseEntity는 Spring에서 제공하는 클래스로, HTTP 응답을 생성하는 데 사용됩니다. 이 글에서는 ResponseEntity를 사용하여 Spring Boot 애플리케이션에서 API 응답을 처리하는 방법에 대해 알아보겠습니다.
ResponseEntity란?
ResponseEntity는 HTTP 응답을 나타내는 클래스입니다. 이 클래스는 응답의 상태 코드, 헤더, 본문을 포함할 수 있습니다. ResponseEntity를 사용하면 컨트롤러에서 다양한 상태 코드와 메시지를 클라이언트에 반환할 수 있습니다.
ResponseEntity 사용하기
1. 성공 응답 보내기
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class MyController {
@GetMapping("/api/data")
public ResponseEntity<String> getData() {
String data = "Hello, World!";
return ResponseEntity.ok(data);
}
}위의 코드에서는 "/api/data" 엔드포인트로 GET 요청이 들어오면 "Hello, World!" 문자열을 성공 응답으로 반환합니다. ResponseEntity.ok() 메서드를 사용하여 HTTP 상태 코드 200을 설정하고 응답 본문으로 데이터를 설정합니다.
2. 클라이언트 에러 처리하기
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class MyController {
@GetMapping("/api/data")
public ResponseEntity<String> getData(@RequestParam String type) {
if (!"valid".equals(type)) {
return ResponseEntity.badRequest().body("Invalid type parameter");
}
String data = "Hello, World!";
return ResponseEntity.ok(data);
}
}위의 코드에서는 "/api/data" 엔드포인트로 GET 요청이 들어오면 type 매개변수의 값이 "valid"이 아닌 경우에는 클라이언트 에러를 반환합니다. ResponseEntity.badRequest() 메서드를 사용하여 HTTP 상태 코드 400을 설정하고 에러 메시지를 반환합니다.
상태코드별 메소드 종류
- 200번대: 성공
- ok(): HTTP 상태 코드 200을 반환하고, 성공적인 응답을 반환합니다.
- created(): 201을 반환하고, 새로운 리소스가 성공적으로 생성되었음을 나타냅니다.
- accepted(): 202을 반환하고, 요청이 수신되었지만 아직 처리되지 않았음을 나타냅니다.
- 300번대: 리다이렉션
- multipleChoices(): HTTP 상태 코드 300을 반환, Client에게 여러 선택지 중 하나를 선택하도록 안내합니다.
- movedPermanently(): 코드 301을 반환하고, 리소스가 영구적으로 새 위치로 이동되었음을 나타냅니다.
- found(): 코드 302를 반환하고, 리소스가 일시적으로 다른 위치에 있음을 나타냅니다.
- 400번대: 클라이언트 오류
- badRequest(): HTTP 상태 코드 400을 반환하고, 클라이언트의 잘못된 요청을 나타내는 응답을 반환합니다.
- unauthorized(): 코드 401을 반환하고, 클라이언트가 인증되지 않았음을 나타내는 응답을 반환합니다.
- forbidden(): 코드 403을 반환하고, 클라이언트가 요청한 리소스에 접근 권한이 없음을 나타내는 응답을 반환합니다.
- 500번대: 서버 오류
- internalServerError(): HTTP 상태 코드 500을 반환하고, 서버에서 예기치 못한 오류가 발생했음을 나타내는 응답을 반환합니다.
- notImplemented(): 코드 501을 반환하고, 요청된 기능이 서버에 구현되지 않았음을 나타낸 응답을 반환합니다.
- serviceUnavailable(): 코드 503을 반환하고, 서버가 현재 요청을 처리할 수 없음을 나타내는 응답을 반환합니다.
ResponseEntity는 Spring Boot 애플리케이션에서 API 응답을 처리하는 강력한 도구입니다. 이 클래스를 사용하여 다양한 상태 코드와 메시지를 클라이언트에 반환할 수 있으며, 클라이언트와의 효과적인 통신을 구현할 수 있습니다. ResponseEntity를 활용하여 안정적이고 유연한 API를 설계할 수 있습니다.
Service -> Controller 관계도
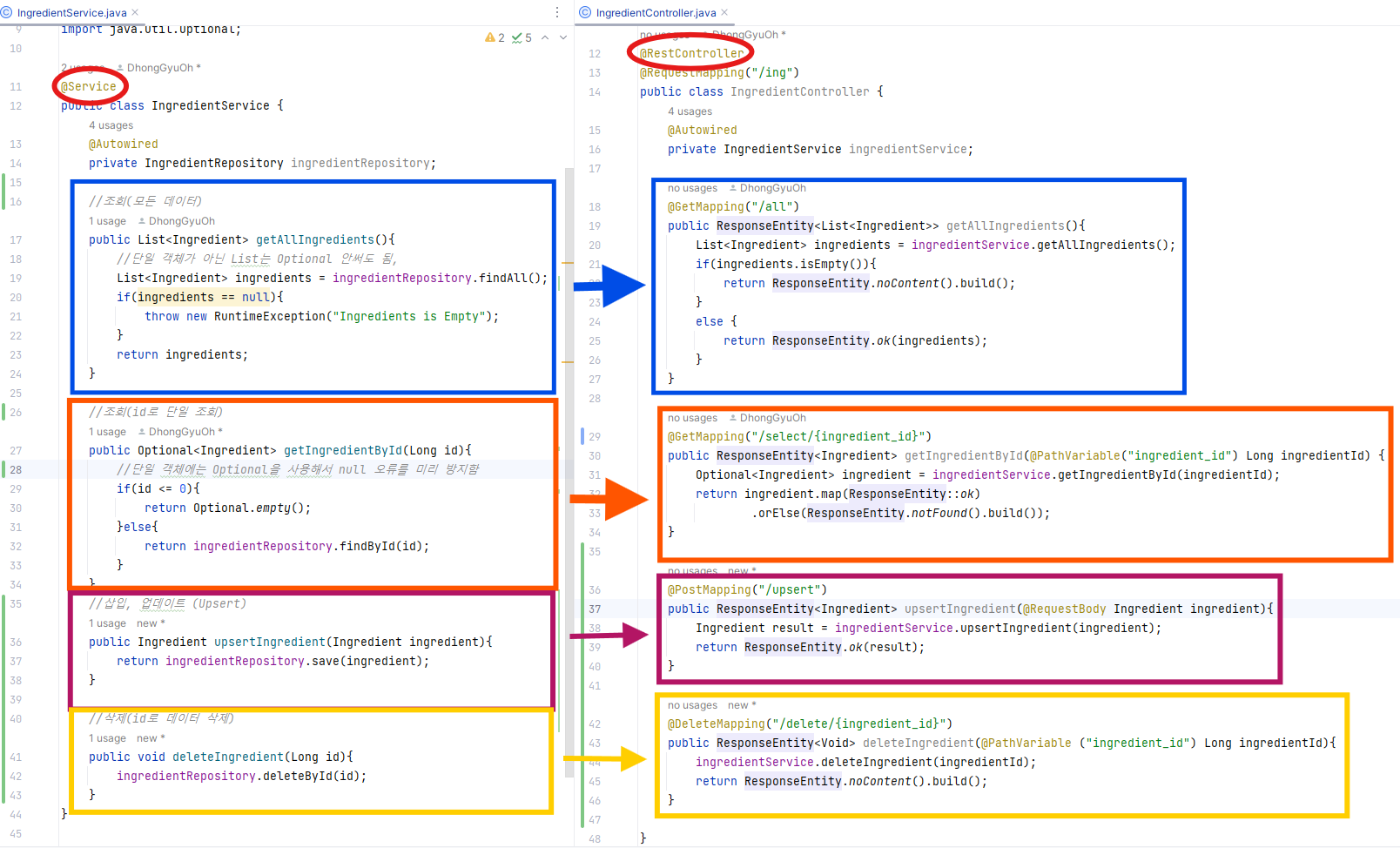
'서버 개발 > Spring Boot' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 7. [Spring Boot] PropertyReferenceException 에러 해결 (Java "_" 언더바 인식 못함 문제) (0) | 2024.04.30 |
|---|---|
| 6. [Spring Boot] application.yml 설정하기 (0) | 2024.04.29 |
| 4. [Spring Boot] Optional 사용 (NullPointerException 방지하기) (0) | 2024.04.16 |
| 3. [Spring Boot] JPA, findAll() 메소드로 전체 Data 가져오기 (0) | 2024.04.15 |
| 2. [Spring Boot] MySQL 연동하기(With JPA) (0) | 2024.04.15 |



